Blogs
Read more about different aspects and implications of this project
ROXANNE Final Conference
—
by Duszynska-Trojanowska, Anna
—
last modified
Dec 14, 2022 09:04 AM
With ROXANNE project coming to an end, one of the tasks in work package dedicated to project dissemination and exploitation was to organize a Final Conference. The preparations for the event started in February 2022 and involved a lot of effort from all partners, especially Capgemini Technology Services as a leader of the work package and the task itself, along with Trilateral Research and IDIAP Research Institute as the project coordinator.
Testimonial by Hellenic Police
—
by Duszynska-Trojanowska, Anna
—
last modified
Dec 09, 2022 09:52 AM
Hellenic Police is proud to be one of 25 partners of the ROXANNE consortium who, along with other Law Enforcement Agencies, industry and academia, joined forces in the fight against terrorism and organized crime.
Introduction of ROXANNE project outputs in the Czech Republic
—
by Duszynska-Trojanowska, Anna
—
last modified
Dec 08, 2022 10:19 AM
As the development of the Autocrime platform is gradually coming to an end, and the software is beginning to take on concrete contours, it seemed appropriate to start introducing it to our colleagues in the security services of the Czech Republic.
Research work in ROXANNE
—
by Duszynska-Trojanowska, Anna
—
last modified
Nov 04, 2022 02:28 PM
Throughout the course of the project, many research topics have been explored by the partners and many publications have already been published in scientific journal publications. Here we provide a brief summary of the different research topics on which partners are currently considering submitting new journal publications.
Making the world a safer place – INTERPOL’s views on the ROXANNE Project
—
by Duszynska-Trojanowska, Anna
—
last modified
Nov 04, 2022 11:56 AM
Today’s crimes are increasingly international and INTERPOL provides a platform for cooperation in the global security architecture by enabling our 195 member countries to work together for a safer world. Through INTERPOL policing capabilities, Law Enforcement Agencies (LEAs) across the world have the ability to exchange data within a dedicated and restricted environment, in accordance with our Rules on the Processing of Data that meet the highest level of international data privacy requirements.
The third and Final Field Test
—
by Duszynska-Trojanowska, Anna
—
last modified
Nov 03, 2022 12:52 PM
During the ROXANNE project, three field tests have been organised. The first field test took place on 30 September 2020 online (due to the COVID-19 pandemic restrictions) and was organised by KEMEA. It presented the preliminary capabilities of the ROXANNE platform i.e., combining speech and text technologies along with network analysis methods. The second field test, was organised in hybrid mode (both onsite and online) by NFI on 8 October 2021, during which the platform’s latest capabilities and case scenarios were demonstrated.
ROXANNE Technology updates – The Autocrime platform
—
by Duszynska-Trojanowska, Anna
—
last modified
Nov 02, 2022 12:18 PM
The Autocrime platform was constantly updated during the last six months integrating additional features and taking into account feedback from LEAs based on their experiences. The latest release of the platform is intended to be installed on users’ machines (e.g., laptop) and supports several Operating Systems; namely Linux Ubuntu, MacOS (including M1 chipsets) and Windows (using a Virtual Machine).
LEA use of outcomes from the ROXANNE project
—
by Duszynska-Trojanowska, Anna
—
last modified
Oct 18, 2022 11:56 AM
With the project approaching its closing stages the focus for all partners is not just a successful completion of a project but more importantly the development of tools and products that will enhance the safety of the public through law enforcement activities, and enhance the commercial viability of the tools for the institutes and companies involved in the project. Every EU funded security research project aims to meet the needs and requirements of the end user, in this case Law Enforcement Agencies (LEAs).
The Analytical Process for Law Enforcement Agencies – From Basics to ROXANNE
—
by Duszynska-Trojanowska, Anna
—
last modified
Sep 28, 2022 11:17 AM
Analysis by Law Enforcement Agencies: The analysis stage of the intelligence process is a key one. Analysis can be described as an in-depth examination of the meaning and essential features of available information. Analysis highlights information gaps, strengths, weaknesses and suggests ways forward.
Changing the Public Sector with Artificial Intelligence
—
by Duszynska-Trojanowska, Anna
—
last modified
Sep 05, 2022 08:40 AM
IT teams of Law Enforcement Agencies (LEAs) are often in an everyday struggle towards transforming the old thinking into the new Artificial Intelligence (AI) way of thinking, with many challenges regarding goals, directors, clients, technologies, and methodologies. The transition from one type of IT project to another is relatively simple, but the AI mindset switch is a completely different thing that requires transformations in so many aspects within the organization. This is a long journey which requires perseverance and a lot of patience. Many LEAs are at the beginning of this track which will yield many incites in the coming years. In this blog post we try to mirror the efforts to grips with the myriad of challenges this field has opened for LEAs and how ROXANNE could help in this direction.
Creating a Real-World Dataset Simulating Organized Crime Communication
—
by Duszynska-Trojanowska, Anna
—
last modified
Aug 01, 2022 01:17 PM
The ROXANNE project is developing a cutting-edge solution to help Law Enforcement Agencies (LEAs) perform extremely efficient investigations through sophisticated use of biometric technologies (such as Phonexia Voice Biometrics), automatic speech recognition, and large-data processing automation—all within the boundaries of a privacy-first legal framework. The last-mentioned point, however, also means a significant challenge for the evaluation of the ROXANNE solution itself. How can one evaluate the solution’s performance in the real world if there is limited real-world data to be used due to privacy, GDPR, and other ethical constraints? This is where the ROXANNE’s unique evaluation dataset comes in.
Does Off-the-Shelf Named Entity Recognition (NER) Techniques work in the context of Criminal Investigation?
—
by Duszynska-Trojanowska, Anna
—
last modified
Jul 25, 2022 08:31 AM
Entity Recognition aims to identify names of organizations, people, and geographic locations. For instance, “I hear Switzerland is beautiful in winters” has a mention of a location “Switzerland” and a time “winters”. It was first proposed at the Message Understanding Conference (MUC-6), since then there has been a significant amount of interest in Named Entity Recognition (NER) and information extraction techniques on textual data for various scientific fields. It is widely used across various fields and sectors to automate the information extraction process, but there has been no significant work to recognize these entities in the context of automatically generated transcripts of telephone calls by using Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR).
Entity Recognition and how it can help LEAs
—
by Duszynska-Trojanowska, Anna
—
last modified
Jun 23, 2022 01:51 PM
Everyday language involves extensively talking about things and places associated to the speakers. While these seem trivial in normal scenarios, the places and people talked about can become exponentially interesting to Law Enforcement Authorities (LEAs) in a criminal scenario.
Voiceprints and their properties
—
by Duszynska-Trojanowska, Anna
—
last modified
Apr 29, 2022 11:06 AM
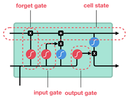
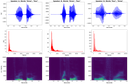
Speaker recognition is a technology that uses computer algorithms to analyze speech patterns and determine the identity of the speaker in a recording. Speaker recognition is an important part of the ROXANNE platform because the identities of speakers in recordings from criminal investigations are usually not known. In state of the art speaker recognition systems, recordings of variable durations are converted to fixed sized vectors [1,2,3], often referred to as voiceprints or speaker embeddings. Given such voiceprints from two recordings, their similarity can be measured to estimate how likely it is that the speaker in both the recordings is the same person. In this post we explain how voiceprints are extracted from audio. We also discuss some of their properties and what information they contain.
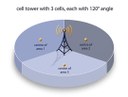
Location traces in criminal investigations
—
by Duszynska-Trojanowska, Anna
—
last modified
Mar 30, 2022 11:29 AM
When reconstructing the events that led up to a crime, establishing the location of a suspect is often of crucial relevance. A suspect’s whereabouts can be informed by tactical and forensic information , and one of the most widely used sources in investigations are mobile phone records that can be provided by telephone network operators. However, these data are hard to analyze and easily misinterpreted. As such, location analysis is part of ROXANNE, a platform for analyzing speech and communication traces.
Privacy-by-Design in ROXANNE technologies
—
by Duszynska-Trojanowska, Anna
—
last modified
Feb 28, 2022 01:39 PM
Privacy is an important ethical, social, and legal issue. Yet, some infringement on a person’s privacy by law enforcement agencies (LEAs) might need to take place for effective criminal investigations; this is generally seen as socially acceptable and in compliance with human rights law when it is necessary, proportionate, and done according to legal rules. As such, there are limitations on LEAs processing data about people’s private lives that need to be respected, and the way we design processing technologies is part of that respect.
The assessment of Roxanne Network’s effectiveness
—
by Duszynska-Trojanowska, Anna
—
last modified
Jan 26, 2022 01:38 PM
For the purpose of Roxanne project, it is important that the tools and analysis developed by the researchers enable a precise reconstruction of the criminal networks. Exactly for this reason, Roxanne includes also a specific task to assess the contribution of the technologies developed by the consortium to the understanding and analysis of criminal networks.
Vocabulary and Language Model Adaptation for Automatic Speech Recognition
—
by Duszynska-Trojanowska, Anna
—
last modified
Dec 21, 2021 08:30 AM
An automatic speech recognition (ASR) system is typically a statistical system using a fixed vocabulary. This means that a word which doesn’t exist in the system’s vocabulary can never be recognized correctly. These words are referred to as out-of-vocabulary words (OOV) and form a major source of errors for ASR. In order to keep the ASR system up-to-date and to decrease the OOV errors, the vocabulary and the language model must be adapted on a regular basis. The language model adaptation component, which will soon be part of the ROXANNE solution, tackles this problem by giving the end-users the opportunity to introduce new words into the vocabulary and to build custom models in a semi-automatic way.
Towards a trustworthy ROXANNE platform
—
by Duszynska-Trojanowska, Anna
—
last modified
Dec 01, 2021 12:00 PM
Funded under the Horizon2020 programme supporting ground-breaking research and advancing European excellence, ROXANNE aims to support law enforcement authorities (LEAs) fight crime and terrorism by facilitating the analysis of criminal data. To this end, the ROXANNE platform combines innovative data analysis capabilities, including speech and language technologies, visual analysis and network analysis, to help identify perpetrators. ROXANNE’s innovation lies in the bi-directional interaction between the multimodal technological processes integrated in the platform. The analysis process further benefits from prior knowledge available to investigators for increased accuracy results that contribute to advancing the case. With Artificial Intelligence (Al) at the core of the ROXANNE platform through the underlying algorithmic models, the project team adopted ethics and privacy by design approach in its research work in order to develop an ethically, legally and socially sound final result.
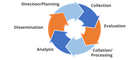
The intelligence cycle and the ROXANNE platform
—
by Duszynska-Trojanowska, Anna
—
last modified
Feb 17, 2022 11:25 AM
During investigations the law enforcement practitioners working on the case need to collect and review evidence and intelligence to reconstruct the committed crime or, in case of an ongoing offense, to understand the “modus operandi” of a criminal group and prosecute its members. This blog posts gives an overview of how the ROXANNE platform supports analysts and investigators in key phases of their work.
Social Network Analysis for Criminology in ROXANNE
—
by Garg, Shivam
—
last modified
Nov 05, 2021 02:56 PM
Social network analysis provides an essential set of analytic tools to study people’s behavior: Social influence analysis, community detection, link prediction, and cross-network analysis are examples of such tools. Law enforcement agencies can benefit from them in criminology. In ROXANNE, we focus on several real crime cases and build a specialized tool for criminology that includes the state-of-the-art methods for each of these options.
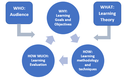
ROXANNE Training Framework: Delivering the training material to end-users through remote (or physical) training sessions
—
by Garg, Shivam
—
last modified
Nov 05, 2021 02:57 PM
Learn facts about learning and our training methodology for effective use of the ROXANNE platform.
Ηow organized crime and cybercrime altered during the COVID-19 period
—
by Garg, Shivam
—
last modified
Nov 04, 2021 02:36 PM
The COVID-19 pandemic is expected to have a multifaceted impact on serious organized crime, particularly cybercrime. Lifestyle changes that arose in response to the restrictions during the epidemic, such as extended teleworking, widespread internet purchasing, and other behaviors, are unlikely to fade once the lockdown is lifted. As a result, cybercriminals will continue to seek ways to exploit these behaviors, either by modifying existing attacks or developing new ones.
Combining computer vision techniques with speech technologies for the fight against crime
—
by Garg, Shivam
—
last modified
Nov 05, 2021 02:58 PM
ROXANNE combines multiple analytics on various modalities (audio, text, image, metadata) to support LEAs in their investigations. In this post, we review how analysts and investigators can benefit from the significant progress achieved in computer vision in recent years, especially when combining it with speech or network analysis.
Dissemination & exploitation efforts in project ROXANNE
—
by Garg, Shivam
—
last modified
May 31, 2021 10:43 AM
ROXANNE project has completed about half of its journey until now. We are happy to share that with the support, feedback, and comments of our readers, stakeholders, end-users, and partners, we have achieved to create a preliminary version of this unique platform. We are certain that this platform will be used ethically for the betterment of society and we are ensuring checks for the same at various steps as well. In this blog, we will discuss some of the recent project updates and explore our efforts and objectives with respect to exploitation.
NLP technologies against online crime
—
by Garg, Shivam
—
last modified
Apr 27, 2021 09:41 AM
Big Data in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) technologies offer new opportunities. The principle is that an extensive amount of data is required for the best result of the scenario of fighting crime ML models. In the ROXANNE project, the technical development targets to significantly enhance the criminal network analysis based on text, speech, language, and video technologies.
ROXANNE Stakeholder Board
—
by Garg, Shivam
—
last modified
Apr 01, 2021 11:00 AM
As an EU-funded collaborative research and innovative project, ROXANNE has been accompanied since its launch by a Stakeholder Board (SB) for independent and methodological advice, counseling the consortium on the practical implementation of its goals, as well as on encountered issues regarding its progress, direction, and outcomes. This external project advisory group is formed of 16 interdisciplinary experts coming from diverse backgrounds, including law enforcement, academia, EU entities, international organisations, fellow research projects, and industry.
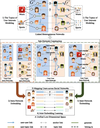
Multimodal networks integration improves the criminal entity network construction with the help of deep neural networks
—
by Garg, Shivam
—
last modified
Nov 05, 2021 02:58 PM
The network integration fuses information from ROXANNE platform component technologies for network analysis. In previous workloads, crime-related networks from different data sources are constructed. We propose a multilayer and cross-network structural analysis to provide methods for integrating information from several investigation cases and linking the data records across these.
Making Natural Language Processing work for Little Training Data
—
by Garg, Shivam
—
last modified
Nov 05, 2021 02:59 PM
In the ROXANNE project we are solving real-world problems which often do not have a large labelled training set. To overcome such data scarcity problems, we use the combination of distant supervision and noise-robust learning algorithms. Distant supervision serves as a way of obtaining a large amount of labelled data in an automatic manner. Such data is however often noisy so that feeding them directly to DNN models will hinder the learning process. Nonetheless, noise-robust learning algorithms will help the models to focus on the correct instances in the training set so that the models will not be affected much by the noise.
The Benefits of Using Automatic Speaker Recognition in LEAs’ Investigative Processes
—
by Garg, Shivam
—
last modified
Nov 05, 2021 03:00 PM
Traditional manually performed forensic analyses are language-dependent and time-consuming, while automatic speaker recognition systems are fast and language-independent (nevertheless, the role of a forensic expert is still irreplaceable for the presentation of the results). There is also other voice biometric information that can be automatically extracted from a person’s voice, such as the gender of a speaker. The bottom line is that current automatic speaker recognition systems, such as the one currently built by the ROXANNE consortium, can greatly improve the analytical work efficiency, enabling law enforcement agencies of any size to investigate faster.
Document Actions